Use the graph below to answer the following questions.Dt is the transactions demand for money, Dm is the total demand for money, and Sm is the supply of money. 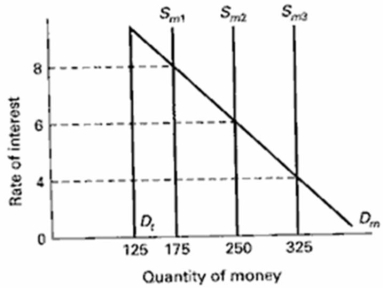 (a) What is the transactions demand for money in this market?
(a) What is the transactions demand for money in this market?
(b) What is the asset demand for money if the interest rate is 4%?
(c) If the money market is in equilibrium at 6%, describe the change that must occur for the equilibrium rate to change to 4%.(d) If the money market is in equilibrium at 6% and the money supply has increased to Sm3, by how much has total demand for money changed?
Definitions:
Neurotransmitter Receptor
A protein molecule on a neuron's surface that reacts to a specific neurotransmitter, influencing neural communication.
Neurotransmitter
Chemical substances released at the end of a nerve fiber by the arrival of a nerve impulse, facilitating the transmission of impulses to another nerve fiber, a muscle fiber, or some other structure.
Plasma Membrane
The lipid bilayer that encloses the cytoplasm of a cell, regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Depolarizing
A process in which a cell's membrane potential becomes less negative, moving towards zero, often leading to an action potential in neurons.
Q1: If Canada doubled its real GDP, it
Q19: Government alters the distribution of income by
Q20: The next three questions refer to the
Q22: Evaluate: A tax system in which those
Q24: What is the difference between the Bank
Q27: What is meant by currency appreciation?
Q48: The Federal government is considering passing an
Q55: What to produce in a market economy
Q57: The development of the Internet and e-mail
Q63: One of the basic economic defences of