Assume that without any taxes the consumption schedule for an economy is as shown in the table.Also assume that investment, net exports, and government expenditures do not change with changes in real GDP. 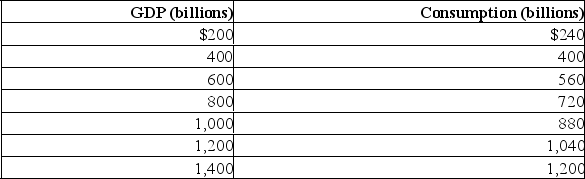 (a) What are the MPC, MPS, and the size of the multiplier?
(a) What are the MPC, MPS, and the size of the multiplier?
(b) Assume a lump-sum tax of $10 billion is imposed at all levels of GDP.Determine consumption and the tax rate at each level of GDP by completing the following table.Is tax regressive, proportional, or progressive? Compare the multiplier under the lump-sum tax with the pre-tax multiplier. 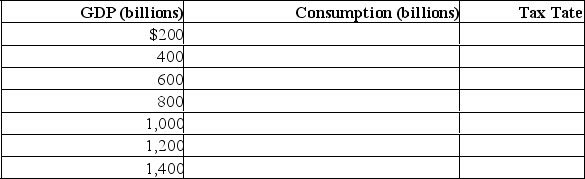 (c) Assume instead that a proportional tax of 10% is imposed at all levels of GDP.Determine consumption at each level of GDP by completing the following table.Compare the multiplier under the proportional tax with the multiplier under the lump-sum tax.Explain why a proportional or progressive tax system contributes to greater economic stability as compared with the lump-sum tax.
(c) Assume instead that a proportional tax of 10% is imposed at all levels of GDP.Determine consumption at each level of GDP by completing the following table.Compare the multiplier under the proportional tax with the multiplier under the lump-sum tax.Explain why a proportional or progressive tax system contributes to greater economic stability as compared with the lump-sum tax. 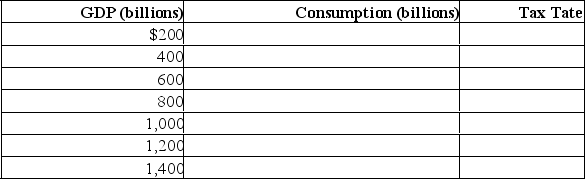
Definitions:
Federal System of Government
A form of governance where power is divided between a central (federal) government and individual state or provincial governments.
Charter of Rights and Freedoms
A foundational document in Canada that guarantees fundamental rights and freedoms to its citizens and residents.
Paramountcy
The principle that when a matter is addressed by both valid federal and provincial legislation and there is a conflict, the federal legislation takes precedence.
Supreme Court of Canada
The highest court in Canada, serving as the final appellate body in the Canadian legal system.
Q9: Draw a market demand curve and indicate
Q10: What adjustments need to be made to
Q13: What are two key facts that serve
Q15: What do economists mean when they say
Q16: What roles do freedom of enterprise and
Q27: What are two reasons why prices might
Q38: What are the net costs of tariffs
Q185: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6686/.jpg" alt=" In the above
Q200: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6686/.jpg" alt=" Refer to the
Q226: Assume that if the interest rate that