Assume that without any taxes the consumption schedule for an economy is as shown in the table.Also assume that investment, net exports, and government expenditures do not change with changes in real GDP. 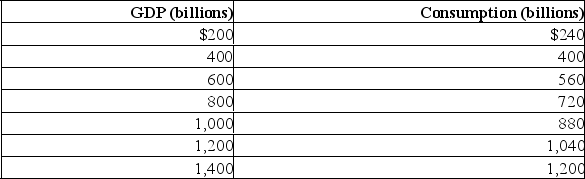 (a) What are the MPC, MPS, and the size of the multiplier?
(a) What are the MPC, MPS, and the size of the multiplier?
(b) Assume a lump-sum tax of $10 billion is imposed at all levels of GDP.Determine consumption and the tax rate at each level of GDP by completing the following table.Is tax regressive, proportional, or progressive? Compare the multiplier under the lump-sum tax with the pre-tax multiplier. 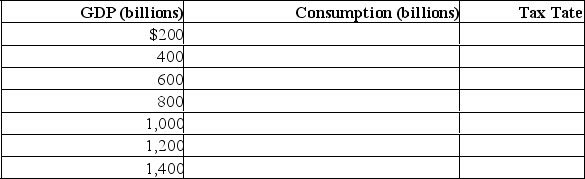 (c) Assume instead that a proportional tax of 10% is imposed at all levels of GDP.Determine consumption at each level of GDP by completing the following table.Compare the multiplier under the proportional tax with the multiplier under the lump-sum tax.Explain why a proportional or progressive tax system contributes to greater economic stability as compared with the lump-sum tax.
(c) Assume instead that a proportional tax of 10% is imposed at all levels of GDP.Determine consumption at each level of GDP by completing the following table.Compare the multiplier under the proportional tax with the multiplier under the lump-sum tax.Explain why a proportional or progressive tax system contributes to greater economic stability as compared with the lump-sum tax. 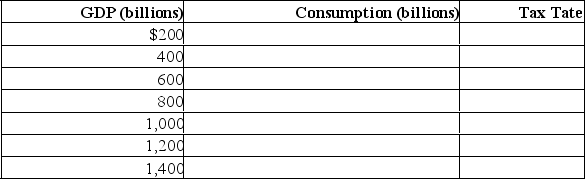
Definitions:
Rudolph Valentino
An Italian actor based in the United States who became a major sex symbol of the silent film era in the early 20th century.
21st-Century
The current century, spanning from 2001 to 2100, characterized by rapid technological advances, globalization, and significant social and environmental challenges.
Unique Allure
A distinctive charm or appeal, often hard to define, that makes something or someone stand out from others.
Film Industry
The sector of entertainment that is involved in the production, distribution, and exhibition of films and movies.
Q1: What is the problem with printing money
Q21: Net investment can be positive, negative, or
Q22: Define "demand."
Q25: In Year 1, the full-employment budget showed
Q26: Using the aggregate demand-aggregate supply (short-run) model,
Q31: Summarize the anti-growth view of economic growth.
Q32: The following table shows marginal costs and
Q48: "The more progressive a tax system, the
Q52: Suppose a fraction of any new loan
Q259: The law of increasing opportunity costs states