Suppose the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply schedules for a hypothetical economy are as shown below:
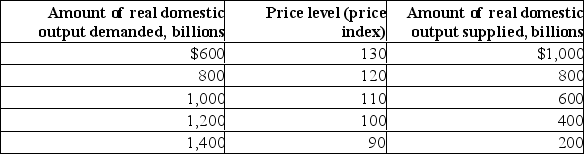 (a) What will be the equilibrium price and real output level in this hypothetical economy? Is this level of real GDP also the full-employment level of output? Explain.(b) Why won't a price level of 110 be the equilibrium price level? Why won't a price level of 130 index be the equilibrium price level?
(a) What will be the equilibrium price and real output level in this hypothetical economy? Is this level of real GDP also the full-employment level of output? Explain.(b) Why won't a price level of 110 be the equilibrium price level? Why won't a price level of 130 index be the equilibrium price level?
(c) Suppose aggregate demand increases by $400 billion at each price level.What will be the new equilibrium price and output levels?
(d) What factors might cause aggregate demand to increase?
Definitions:
Trade Discounts
Discounts given to buyers that generally are based on the quantity purchased.
Net Price
The real cost incurred for a product or service once all discounts, rebates, or allowances have been subtracted.
Complement Rates
In probability, the complement of an event's rate, representing the likelihood of the event not occurring.
Net Price
The actual price paid for a product or service after subtracting any discounts, rebates, or other deductions from the list or sticker price.
Q1: How does a fixed exchange rate system
Q1: Identify the two major ways economic growth
Q2: What were the approximate average incomes of
Q5: What happens to the money supply when
Q9: What conditions are necessary for economic competition
Q17: When would a fixed based price index
Q22: Most economists regard investment demand as being
Q24: How do protectionist policies affect consumers, workers,
Q26: The total demand for money is equal
Q164: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6686/.jpg" alt=" Refer to the