In the below diagram assume that the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 in year 1 to AD2 in year 2, only to fall back to AD1 in year 3. 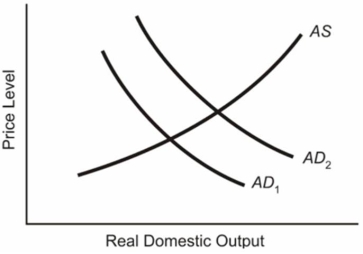 (a) Explain what will happen to the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real GDP from year 1 to year 2.(b) Locate the new position in year 3 on the assumption that prices and wages are completely flexible downward.Label this position, Pb and GDPb for the price level and real GDP respectively.(c) Locate the new position in year 3 on the assumption that prices and wages are completely inflexible downward.Label this position, Pc and GDPc for the price level and real GDP respectively.
(a) Explain what will happen to the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real GDP from year 1 to year 2.(b) Locate the new position in year 3 on the assumption that prices and wages are completely flexible downward.Label this position, Pb and GDPb for the price level and real GDP respectively.(c) Locate the new position in year 3 on the assumption that prices and wages are completely inflexible downward.Label this position, Pc and GDPc for the price level and real GDP respectively.
Definitions:
Market Value at Split-Off Method
A method used to allocate joint costs based on the market value of products at the point of separation in a production process.
Joint Costs
Joint costs are costs incurred during the process of producing two or more products simultaneously, where such costs cannot be easily attributed to each product individually.
Cut Boards
The processed lumber cut into specific lengths or sizes, typically for use in construction or carpentry.
Physical Units Method
An approach in accounting used to allocate joint costs based on the proportional physical quantities of the output produced at a split-off point.
Q4: What is the relationship between actual investment,
Q11: Refer to Figure 9.4. An increase in
Q14: Suppose the Second National Bank has the
Q18: Explain the difference between nominal and real
Q23: Suppose a producer sells 1,000 units of
Q26: Of all the reason for protests against
Q33: Explain the effect of a cut in
Q152: Refer to Figure 9.5. Suppose the economy
Q164: If the marginal propensity to consume is
Q182: Sticky prices cause an economic coordination problem