The graphs below refer to two separate product markets.Assume that society's optimal level of output in each market is Q0 and that government purposely shifts the market supply curve from S to S1in diagram (a) and from S to S2 in diagram (b) .We can conclude that the government is correcting for: 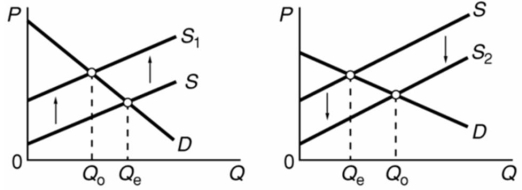
Definitions:
Confirmation Bias
The tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms one's preexisting beliefs or hypotheses.
Gambler's Fallacy
The erroneous belief that if a particular event occurs more frequently than normal during the past, it is less likely to happen in the future, or vice versa, in situations that are truly random.
Ignoring Base Rates
Ignoring base rates is a cognitive bias that involves disregarding or underestimating general information (base rates) in favor of specific individual information when making decisions or judgments.
Availability Bias
A cognitive bias that causes people to overestimate the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory, often leading to skewed decision-making.
Q12: Net exports are negative when:<br>A)a nation's imports
Q16: One condition for individual bargaining to occur
Q25: The basic reason for the production of
Q79: Some people argue that the three main
Q93: Which of the following will cause a
Q133: From an economic perspective, when consumers leave
Q135: Graphically, the market supply curve is:<br>A)steeper than
Q185: Following is data for a hypothetical economy.The
Q193: Which is a determinant of supply?<br>A)tastes and
Q247: An "increase in the quantity demanded" means