Suppose the potential level of real GDP for a hypothetical economy is $250 and the price level (P) initially is 100.Use the following short-run aggregate supply schedules below to answer the questions. 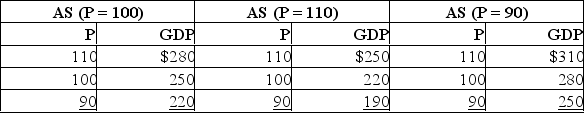 (a) What will be the short-run level of real GDP if the price level rises unexpectedly from 100 to 110 because of an increase in aggregate demand? Falls unexpectedly from 100 to 90 because of a decrease in aggregate demand? Explain each situation.(b) What will be the long-run level of real GDP when the price level rises from 100 to 110? Falls from 100 to 90? Explain each situation.
(a) What will be the short-run level of real GDP if the price level rises unexpectedly from 100 to 110 because of an increase in aggregate demand? Falls unexpectedly from 100 to 90 because of a decrease in aggregate demand? Explain each situation.(b) What will be the long-run level of real GDP when the price level rises from 100 to 110? Falls from 100 to 90? Explain each situation.
Definitions:
Capital Budgeting
The process businesses use to evaluate and select long-term investments that are expected to yield returns over a period of time.
Marginal Cost
The increase in total cost that arises from producing one additional unit of a product or service.
Forecasted Cost
An estimate of the expenses that will be incurred on a project or by a company in a future period.
Average Cost
The total cost of goods available for sale divided by the total number of units available for sale, determining an inventory valuation.
Q3: Describe the characteristics of the short-run aggregate
Q5: Explain the relationship between the current account
Q11: What are the reasons for improved resource
Q17: What is the problem associated with the
Q20: A positive statement is concerned with:<br>A)some goal
Q23: Economists:<br>A)always put the independent variable on the
Q38: What is Securitization and what are its
Q94: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6686/.jpg" alt=" Refer to the
Q98: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6686/.jpg" alt=" Refer to the
Q160: Assume that if the interest rate that