The total demand for money is equal to the transactions demand plus the asset demand for money.(a) Assume that each dollar held for transactions purposes is spent on the average five times per year to buy final goods and services.If nominal GDP is $800 billion, what is the transactions demand?
(b) The table below shows the asset demand at certain rates of interest.Using your answer to part (a), complete the table to show the total demand for money at various rates of interest. 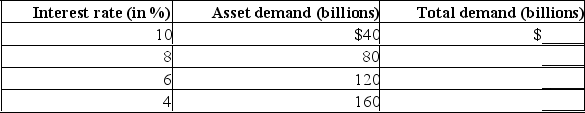 (c) If the money supply is $240 billion, what will be the equilibrium rate of interest?
(c) If the money supply is $240 billion, what will be the equilibrium rate of interest?
(d) If the money supply rises, will the equilibrium rate of interest rise or fall?
(e) If GDP rises, will the equilibrium rate of interest rise or fall?
Definitions:
N-butanol
A four-carbon linear alcohol with the formula C4H9OH, used as a solvent and in the synthesis of various organic compounds.
Hydrochloric Acid
A strong, corrosive acid consisting of hydrogen and chlorine (HCl), widely used in industry and research for various applications, including metal cleaning and pH adjustment.
Lucas Reagent
A chemical reagent used to classify alcohols of low molecular weight based on their reactivity, comprising zinc chloride in concentrated hydrochloric acid.
Alcohol
Alcohol refers to a group of organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to a carbon atom.
Q7: Economy growth matters? Either support or critic
Q13: Positive statements are expressions of value judgments.
Q26: Use the following data to answer the
Q26: In Year 1, the full-employment budget showed
Q30: Evaluate the statement: "Inflation only benefits the
Q33: Trace the cause-effect chain that results from
Q42: Use the figures in the table below
Q76: The demand for commodity X is represented
Q219: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6686/.jpg" alt=" Refer to the
Q248: Economic models:<br>A)are of limited use because they