Assume that without any taxes the consumption schedule for an economy is as shown in the table.Also assume that investment, net exports, and government expenditures do not change with changes in real GDP. 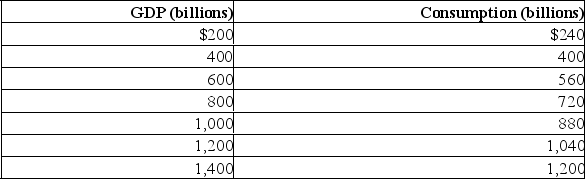 (a) What are the MPC, MPS, and the size of the multiplier?
(a) What are the MPC, MPS, and the size of the multiplier?
(b) Assume a lump-sum tax of $10 billion is imposed at all levels of GDP.Determine consumption and the tax rate at each level of GDP by completing the following table.Is tax regressive, proportional, or progressive? Compare the multiplier under the lump-sum tax with the pre-tax multiplier. 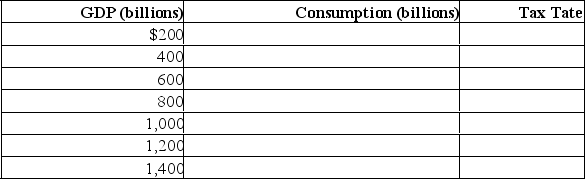 (c) Assume instead that a proportional tax of 10% is imposed at all levels of GDP.Determine consumption at each level of GDP by completing the following table.Compare the multiplier under the proportional tax with the multiplier under the lump-sum tax.Explain why a proportional or progressive tax system contributes to greater economic stability as compared with the lump-sum tax.
(c) Assume instead that a proportional tax of 10% is imposed at all levels of GDP.Determine consumption at each level of GDP by completing the following table.Compare the multiplier under the proportional tax with the multiplier under the lump-sum tax.Explain why a proportional or progressive tax system contributes to greater economic stability as compared with the lump-sum tax. 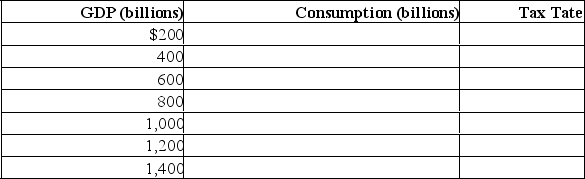
Definitions:
Pauper Labor Fallacy
The incorrect belief that importing goods from countries with lower wage levels hurts the economy of a country with higher wage levels.
Sweatshop Labor Fallacy
The misconception that sweatshop labor is entirely harmful and provides no benefit to workers in developing countries.
Heckscher-Ohlin Theory
An economic theory that suggests countries export what they can most efficiently and abundantly produce.
Absolute Advantage
The ability of a country, company, or individual to produce a good or provide a service more efficiently than competitors.
Q3: Complete the accompanying table. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6686/.jpg" alt="Complete
Q3: Why does aggregate demand shift outward by
Q3: Explain the demand factor in economic growth.
Q4: The table below contains hypothetical international balance
Q8: Why has international trade grown rapidly since
Q11: Explain how the dollar price of an
Q13: What is the effect of increase in
Q16: "If taxes and government spending are increased
Q26: In Year 1, the full-employment budget showed
Q110: A production possibilities curve illustrates:<br>A)scarcity.<br>B)market prices.<br>C)consumer preferences.<br>D)the