After treating cells with a mutagen, you isolate two mutants.One carries alanine and the other carries methionine at a site in the protein that normally contains valine.After treating these two mutants again with mutagen, you isolate mutants from each that now carry threonine at the site of the original valine (see Figure 7-67).Assuming that all mutations caused by the mutagen are due to single nucleotide changes, deduce the codons that are used for valine, alanine, methionine, and threonine at the affected site. 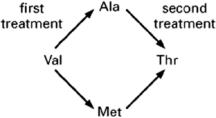
Figure 7-67 The Genetic Code
U C A G U UUU Phe (F) UUC - UUA Leu (L) UUG - CUU Leu (L) CUC - CUA - CUG − AUU Ile (I) AUC - AUA - AUG Met (M) GUU Val (V) GUC - GUA - GUG - C UCU Ser (S) UCC - UCA – UCG - CCU Pro (P) CCC - CCA - CCG − ACU Thr (T) ACC - ACA - ACG - GCU Ala (A) GCC - GCA - GCG - A UAU Tyr (Y) UAC - UAA Stop UAG Stop CAU His (H) CAC - CAA Gin (Q) CAG − AAU Asn (N) AAC - AAA Lys (K) AAG - GAU Asp (D) GAC - GAA Glu (E) GAG - G UGU Cys (C) UGC - UGA Stop UGG Trp (W) CGU Arg (R) CGC - CGA - CGG − AGU Ser (S) AGC - AGA Arg (R) AGG - GGU Gly (G) GGC - GGA - GGG -
Table 7-29
Cannabis
A plant species, of which marijuana and hemp are varieties, used for medicinal and recreational purposes due to its psychoactive properties.
Cognitive-Behavioural
A therapeutic approach that aims to solve problems concerning dysfunctional emotions, behaviors, and cognitions through a goal-oriented, systematic procedure.
Vigorous Activity
Physical activity that is intense enough to significantly raise the heart rate and increase breathing.
Insomnia
A common sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or obtaining restorative sleep.
