After treating cells with a mutagen, you isolate two mutants.One carries alanine and the other carries methionine at a site in the protein that normally contains valine.After treating these two mutants again with mutagen, you isolate mutants from each that now carry threonine at the site of the original valine (see Figure 7-67).Assuming that all mutations caused by the mutagen are due to single nucleotide changes, deduce the codons that are used for valine, alanine, methionine, and threonine at the affected site. 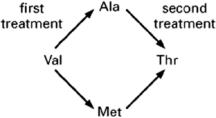
Figure 7-67 The Genetic Code
U C A G U UUU Phe (F) UUC - UUA Leu (L) UUG - CUU Leu (L) CUC - CUA - CUG − AUU Ile (I) AUC - AUA - AUG Met (M) GUU Val (V) GUC - GUA - GUG - C UCU Ser (S) UCC - UCA – UCG - CCU Pro (P) CCC - CCA - CCG − ACU Thr (T) ACC - ACA - ACG - GCU Ala (A) GCC - GCA - GCG - A UAU Tyr (Y) UAC - UAA Stop UAG Stop CAU His (H) CAC - CAA Gin (Q) CAG − AAU Asn (N) AAC - AAA Lys (K) AAG - GAU Asp (D) GAC - GAA Glu (E) GAG - G UGU Cys (C) UGC - UGA Stop UGG Trp (W) CGU Arg (R) CGC - CGA - CGG − AGU Ser (S) AGC - AGA Arg (R) AGG - GGU Gly (G) GGC - GGA - GGG -
Table 7-29
Understand the concept of errorless discrimination training and its applications.
Identify the interchangeability of Pavlovian occasion setters with discriminative stimuli.
Comprehend the process and stages of discrimination learning.
Analyze the role of excitatory and inhibitory processes in discrimination learning and generalization gradients.
Congressional Delegation
Congressional delegation refers to the process by which Congress grants specific powers to administrative agencies or the executive branch of government, often seen in the context of regulatory authority.
Core Purpose
The fundamental reason for an organization's existence, beyond just making money, which guides its operations and priorities.
Administrative Agencies
Entities established by governments to enforce and administer specific laws and regulations.
Law-Interpreting Power
The authority to analyze and determine the meaning of laws and legal principles, often attributed to courts or judges.
