The ethylene response in plants involves a dimeric transmembrane receptor.When the receptor is not bound to ethylene, the receptor binds to and activates a protein kinase, which activates an intracellular signaling pathway that leads to the degradation of a transcriptional regulator important for transcribing the ethylene-responsive genes (see Figure 16-33) .You discover a phosphatase that is important for ethylene signaling, and you name it PtpE.Plants lacking PtpE never turn on ethylene-responsive genes, even in the presence of ethylene.You find that PtpE dephosphorylates serine 121 on the transcriptional regulator.Furthermore, plants lacking PtpE degrade the transcriptional regulator in the presence of ethylene. (A) 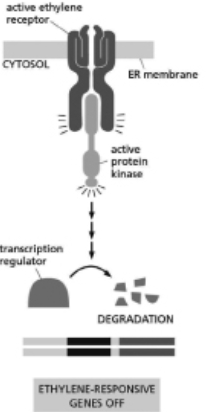
(B) 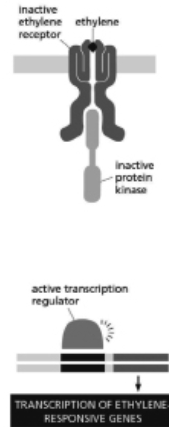
Figure 16-33
Which of the following statements is inconsistent with your data?
Definitions:
Null Hypothesis
A hypothesis in statistical testing that suggests there is no statistical significance between the specified sets of observations, effectively stating that any observed difference is the result of random chance.
Level of Significance
A threshold in hypothesis testing that determines whether an observed effect is statistically significant.
Diverse Individuals
People who exhibit differences in various attributes such as cultural background, race, religion, gender identity, and life experiences.
Sample Size
The number of individuals or observations included in a study, which can significantly impact the statistical power and conclusions drawn.
Q22: Which of the following was NOT among
Q31: A malignant tumor is more dangerous than
Q32: Which of the following statements is TRUE?<br>A)Phospholipids
Q33: Which of the following statements describes the
Q34: The endothelial cells found closest to the
Q56: The oxygen-dependent reactions required for cellular respiration
Q60: Somatic cells _.<br>A)are not necessary for sexual
Q60: Your friend is intrigued by Cdks and
Q62: Cells use membranes to help maintain set
Q63: MPF activity was discovered when cytoplasm from