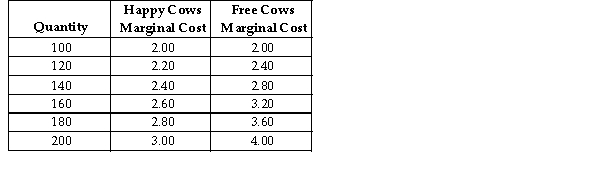
 Happy Cows and Free Cows are two separate perfectly competitive dairy farms. The table above shows the respective firms' marginal cost at various production levels.
Happy Cows and Free Cows are two separate perfectly competitive dairy farms. The table above shows the respective firms' marginal cost at various production levels.
-Refer to the table above. Suppose the perfectly competitive market for dairy products had a 40 percent chance of a high price of $3.00 and a 60 percent chance of a low price of $2.00. However, both Happy Cows and Free Cows have revised their probabilities and now believe that the probability of a high price of $3.00 is 80 percent and the probability of a low price of $2.00 is 20 percent. If the managers of Happy Cows want to maximize expected profit based on the new probabilities by how much will they change the quantity produced?
Definitions:
Marginal Cost
The increase in costs resulting from the manufacturing of one extra good or service.
Dominant Price Leader
A firm that has the largest market share within an industry and whose pricing decisions are often followed by other firms in the market.
Monopolist
An entity, individual, or company that is the sole supplier of a particular commodity or service in a market, often resulting in the power to control prices and market conditions.
Market Demand
The aggregate amount of a product or service that every customer in a market is prepared and able to buy at different price levels.
Q11: Economies of scale are achieved is the
Q17: All else equal, the sooner a depreciation
Q20: If a competitive market is producing at
Q34: For a particular product the Qd =
Q92: If an increase in production lowers your
Q100: The R2 of a regression ranges from_
Q103: Managers can reduce the probability of product
Q123: If a six- sided die is rolled
Q141: If the price of a firm's product
Q152: Refer to the table above. Busy Betty