Use Euler's method with the step size of 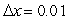 to approximate solution to the initial-value problem
to approximate solution to the initial-value problem 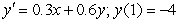 at
at 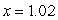 .
.
Definitions:
Gross Margin
represents the difference between revenue and cost of goods sold divided by revenue, showcasing the percentage of sales that exceeds the cost of goods sold.
Arbitrary Allocation
The distribution of indirect costs to specific cost objects without a clear or direct basis, often based on convenience or convention rather than actual usage or benefits derived.
Common Cost
A cost that is incurred to support a number of cost objects but that cannot be traced to them individually. For example, the wage cost of the pilot of a 747 airliner is a common cost of all of the passengers on the aircraft. Without the pilot, there would be no flight and no passengers. But no part of the pilot’s wage is caused by any one passenger taking the flight.
Variable Costing
A costing method that includes only variable production costs (costs that change with the level of output) in product costs, excluding fixed manufacturing overhead.
Q10: What is the proportion of the population
Q21: Name at least five key changes that
Q47: What is the solution to the following
Q63: Evaluate <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6988/.jpg" alt="Evaluate .
Q93: Use Endpaper Tables to evaluate <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6988/.jpg"
Q173: Evaluate <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6988/.jpg" alt="Evaluate ."
Q222: Answer true or false. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6988/.jpg" alt="Answer
Q241: Find the area of the surface generated
Q249: Determine whether or not the following series
Q279: Use a suitable Maclaurin Series to estimate