Evaluate 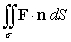 where F(x, y, z) = 2 i - z j + y k and is that portion of the paraboloid x = y2 + z2 between x = 0 and x = 4. The surface is oriented by forward unit normals.
where F(x, y, z) = 2 i - z j + y k and is that portion of the paraboloid x = y2 + z2 between x = 0 and x = 4. The surface is oriented by forward unit normals.
Definitions:
Broad Sense Heritability
The proportion of the total phenotypic variance of a trait that is attributable to genetic variance, where genetic variance is represented in its entirety as a single value (that is, genetic variance is not broken down into different components).
Narrow Sense Heritability
Narrow sense heritability is a measure of the proportion of phenotypic variance in a trait that can be attributed to additive genetic variance among individuals in a population.
Additive Effects
The cumulative impact of individual genes on a phenotype, where the total effect is the sum of the effects of each gene.
Dominance Effects
Phenomena where the phenotype of the heterozygote is closer to that of one of the homozygotes due to the dominant influence of one allele over another.
Q17: F (x, y, z) = 5xyz i
Q42: Let r(t) = (t<sup>3</sup> + 2)i +
Q76: Let y = x<sup>2</sup> + 12. Find
Q82: Find the surface area of the portion
Q84: Locate all relative maxima, relative minima, and
Q104: Answer true or false. A plane
Q106: Use a differential to approximate sin 36°.
Q114: Find the x-coordinates of all points
Q142: If y = (cot t)<sup>2</sup><sup>t</sup>, find <img
Q597: Answer true or false. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6988/.jpg" alt="Answer