Consider the following calculations for a one-way analysis of variance from a completely randomized design with 20 total observations equally divided into 4 treatments. The response variable is sales in millions of dollars, and the four treatment levels represent the four regions that the company serves.
MSE = 101.25 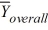 = 39
= 39 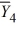 = 33
= 33 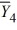 = 43
= 43 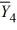 = 49
= 49 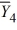 = 31
= 31
Perform a pairwise comparison between treatment mean 3 and treatment mean 4 by computing a Tukey 90 percent simultaneous confidence interval.
Definitions:
Job A496
A specific project or order identifier, representing a unique job or task within a job costing system.
Machine Hours
A measurement of the amount of time a machine is operated during a given period.
Variable Manufacturing Overhead
Costs of manufacturing that vary with the level of production, such as supplies and utilities used in the production process.
Job A496
This is a reference to a specific task, project, or work order within a job costing system, identified by the code A496.
Q7: In multiple regression analysis, which one of
Q39: The HR manager of a major office
Q47: Because multiple regression models consist of multiple
Q59: Consider the following partial computer output from
Q60: The normal plot is a residual plot
Q60: The following frequency table summarizes the ages
Q94: According to a national survey, the average
Q102: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7056/.jpg" alt=" Consider the randomized
Q120: In testing the difference between the means
Q129: Looking at four different diets, a researcher