Consider the following calculations for a one-way analysis of variance from a completely randomized design with 20 total observations equally divided into 4 treatments.
MSE = 101.25 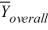 = 39
= 39 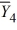 = 33
= 33 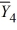 = 43
= 43 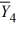 = 49
= 49 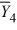 = 31
= 31
Compute a 95 percent confidence interval for the first treatment mean.
Definitions:
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars that are the most basic form of carbohydrates, serving as energy sources and building blocks for more complex sugars.
Disaccharides
Carbohydrates composed of two monosaccharide molecules bonded together, such as sucrose and lactose, which are used by organisms as energy sources.
Polysaccharide
A carbohydrate molecule consisting of long chains of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages.
Sugars
Carbohydrates that are sweet to taste, soluble in water, and used as a source of energy by living organisms.
Q4: As the margin of error decreases, the
Q15: The following results were obtained from a
Q23: In logistic regression, the difference between a
Q57: What are used to avoid overfitting in
Q75: You want to estimate the proportion of
Q79: When using the chi-square goodness-of-fit test, if
Q80: A mail-order business prides itself in its
Q83: The HR manager of a major office
Q103: When the null hypothesis is true, there
Q118: In a 2-way ANOVA, treatment is considered