Consider the following calculations for a one-way analysis of variance from a completely randomized design with 20 total observations equally divided into 4 treatments. The response variable is sales in millions of dollars and the four treatment levels represent the four regions that the company serves.
MSE = 101.25 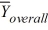 = 39
= 39 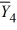 = 33
= 33 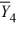 = 43
= 43 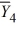 = 49
= 49 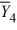 = 31
= 31
Perform a pairwise comparison between treatment mean 1 and treatment mean 4 by computing a Tukey 95 percent simultaneous confidence interval.
Definitions:
Capacity Shortage
A situation where the demand for a company's output exceeds its production capacity.
Margin Reduction
The decrease in the difference between the selling price of a product and its cost, often due to increased costs or reduced selling prices.
Backup Source
An alternative or supplementary source, often used for data, power, or supply chain redundancy, to ensure continuity in the event of primary source failure.
Production Capacity
The maximum amount of goods or services that can be produced by a facility within a specific time frame under normal working conditions.
Q12: A local tire dealer wants to predict
Q57: At the end of 1990, 1991, and
Q60: The normal plot is a residual plot
Q74: In an opinion survey, a random sample
Q74: Consider a two-way analysis of variance experiment
Q81: The tolerance interval of 95.44 percent is
Q83: The HR manager of a major office
Q99: A U.S.-based company offers an online proficiency
Q107: The following frequency table summarizes the ages
Q115: When we carry out a chi-square test