A fast-food company uses two management-training methods. Method 1 is a traditional method of training, and Method 2 is a new and innovative method. The company has just hired 31 new management trainees. 15 of the trainees are randomly selected and assigned to the first method, and the remaining 16 trainees are assigned to the second training method. After three months of training, the management trainees take a standardized test. The test was designed to evaluate their performance and learning from training. The sample mean score and sample standard deviation of the two methods are given below. The management wants to determine if the company should implement the new training method.
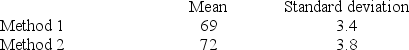 What is the absolute value of the rejection point (critical value of the test statistic) at α = .01?
What is the absolute value of the rejection point (critical value of the test statistic) at α = .01?
Definitions:
Thought Disorder
A disturbance in the organization and expression of thought, often observed as fragmented or disconnected speech, indicative of certain mental illnesses.
Bleuler
A Swiss psychiatrist known for his work in the early 20th century, notably for coining the term "schizophrenia."
Schizophrenia
A severe mental disorder characterized by disturbances in thought, perception, and behavior, leading to a disconnect from reality.
Delusions of Grandeur
A belief in one's exaggerated sense of importance, power, knowledge, or identity, often found in manic or psychotic conditions.
Q32: When we test H<sub>0</sub>: μ<sub>1</sub> − μ<sub>2</sub>
Q41: A researcher has used a one-way analysis
Q54: _ is an iterative variable selection procedure
Q56: Consider an engine parts supplier and suppose
Q58: The weight of a product is measured
Q66: χ<sup>2</sup><sub>α</sub> is the point on the vertical
Q76: A manufacturer of salad dressings uses machines
Q80: A vitamin-water manufacturer wants to compare the
Q117: An experiment consists of 400 observations and
Q141: The following time-sequenced observations of actual and