An MBA admissions officer wishes to predict an MBA applicant's grade point average (GPA) for the MBA program on the basis of the applicant's score on the Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) and their undergraduate GPA (UGPA) . The admissions officer used a random sample of previously admitted applicants to build a regression tree that can be used to predict the MBA GPAs of future MBA students. Below is the final regression tree. 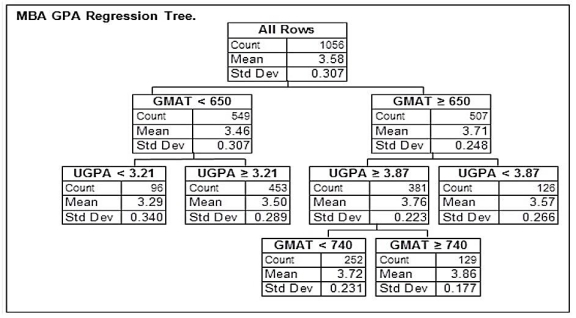 The school awards a Dean's Scholarship to admitted applicants who it predicts will earn a GPA of 3.85 or higher in the MBA program. An MBA applicant has an undergraduate GPA of 3.91. Based on this regression tree, which of the following GMAT scores is the lowest this applicant can earn to qualify for the Dean's Scholarship?
The school awards a Dean's Scholarship to admitted applicants who it predicts will earn a GPA of 3.85 or higher in the MBA program. An MBA applicant has an undergraduate GPA of 3.91. Based on this regression tree, which of the following GMAT scores is the lowest this applicant can earn to qualify for the Dean's Scholarship?
Definitions:
Population Proportions
The ratio of members in a statistical population that have a particular attribute or characteristic.
Type I Error
A statistical error that occurs when a true null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected.
Type II Error
The error that occurs when a statistical test fails to reject a false null hypothesis, incorrectly concluding that there is no effect or difference when there is.
Null Hypothesis
A default position that there is no association between two measured phenomena or no difference among groups being compared.
Q6: The geometric mean growth rate of sales
Q32: In a statistical study, the random variable
Q32: The equation for the variance of the
Q47: Mutually exclusive events have a nonempty intersection.
Q49: Compute the sample standard deviation of the
Q55: New car owners were asked to evaluate
Q72: If events A and B are mutually
Q96: The internal auditor for your company believes
Q117: Suppose you randomly select 3 DVDs from
Q138: The time between breakdowns of an alarm