Consider the following linear programming problem: Maximize:  Subject to:
Subject to: 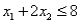
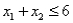
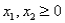 The above linear programming problem
The above linear programming problem
Definitions:
Income From Operations
The earnings of a business generated from its regular business operations, excluding revenues and expenses from non-operational activities.
Operating Expenses
Costs associated with the day-to-day functions of a business, excluding costs directly related to product manufacturing or service delivery.
Revenues
The total income earned by a company for selling its goods or services before any costs or expenses are deducted.
Gross Profit
The difference between sales revenue and the cost of goods sold before deducting overhead, payroll, taxes, and interest payments.
Q12: A play's components and its timeline are
Q14: When we maximize or minimize the value
Q24: Deming said that we should utilize work
Q29: Which of the following statements are false
Q30: In aggregate planning models,the number of workers
Q38: A tornado graph lets us see which
Q40: A company blends silicon and nitrogen to
Q59: The F distribution is a skewed distribution
Q59: Non-truthful response is a particular problem when<br>A)sensitive
Q78: In a transshipment problem,shipments<br>A)can occur between any