The probabilities shown in a table with two rows, 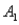 and
and 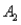 and two columns,
and two columns, 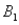 and
and 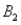 ,are as follows: P(
,are as follows: P( 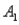 and
and 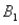 ) = 0.10,P(
) = 0.10,P( 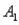 and
and 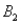 ) = 0.30,P(
) = 0.30,P( 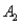 and
and 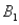 ) = 0.05,and P(
) = 0.05,and P( 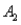 and
and 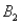 ) = 0.55.Then P(
) = 0.55.Then P( 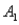 |
| 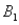 ) ,calculated up to two decimals,is
) ,calculated up to two decimals,is
Definitions:
Form Utility
The value added to products through the process of transformation, creating a more desirable product for consumers.
Place Utility
The value added to products by having them available at a location where they are needed or wanted.
Exchange
A platform or process where goods, services, or securities are traded between two parties.
Wisconsin
A U.S. state located in the north-central United States, in the Midwest and Great Lakes regions, known for its dairy production and manufacturing industries.
Q26: All of the following are true EXCEPT:<br>A)Nearly
Q28: Aulette cites Bem's recommendations for parents to
Q32: Tornado graphs and spider graphs can be
Q35: Which race ethnicity group constitutes the largest
Q40: Sample evidence is statistically significant at the
Q40: Systematic sampling is generally similar to simple
Q66: Two or more events are said to
Q71: The sampling method in which a population
Q82: There are two types of random variables,they
Q94: Conditional probability is the probability that an