Assume that you grew a culture of E. coli for many generations in medium containing 15N (from the ammonium ion), a heavy isotope of nitrogen. You extract DNA from a portion of the culture and determine its density to be 1.723 gm/cm3 (call this sample
A). You then wash the remaining E. coli cells and grow them for one generation in 14N, extract the DNA from a portion of the culture, and determine its density to be 1.715 gm/cm3 (call this sample
B). You let the culture grow for one more generation in 14N, and extract the DNA (call this sample
C) is then heated to completely denature the double-stranded structures, cooled quickly (to keep the strands separate), and subjected to ultracentrifugation. Present the centrifugation profiles for heat-denatured DNA (samples A, B, and
C) that you would expect. Use the graph below. (Note: Although not the case, assume that single-stranded DNA has the same density as double-stranded DNA.)
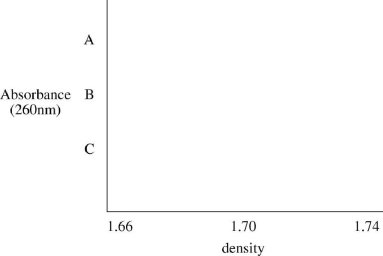
C). Each sample of DNA (A, B, and
Definitions:
Postpartum Depression
Characteristic of women who have such strong feelings of sadness, anxiety, or despair that they have trouble coping with daily tasks during the postpartum period.
Symptoms
Signs or manifestations of a disease or disorder experienced by an individual, which are indicative of an underlying condition.
Challenges
Difficult situations that require a response or adaptation; problems that test one's ability, skill, or determination.
Organogenesis
The phase during embryonic development in which the organs of the body are formed.
Q4: Immediately after fertilization of a Drosophila egg,
Q6: In what way do segregational petite mutations
Q8: A protein is 300 amino acids long.
Q9: When considering the structure of DNA, we
Q21: Intron frequency varies considerably among eukaryotes. Provide
Q28: The relationship between codon and anticodon can
Q37: Early in the 1900s, Sir Archibald Garrod
Q39: List three general pathways in which eukaryotic
Q41: Conditional mutations are more likely to result
Q48: Of the following three types of nucleic