A small disk of radius R1 is fastened coaxially to a larger disk of radius R2.The combination is free to rotate on a fixed axle, which is perpendicular to a horizontal frictionless table top, as shown in the overhead view below.The rotational inertia of the combination is I.A string is wrapped around the larger disk and attached to a block of mass m, on the table.Another string is wrapped around the smaller disk and is pulled with a force as shown.The tension in the string pulling the block is: 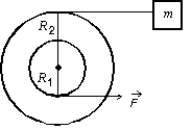
Definitions:
Semicircular Canals
Structures located in the inner ear that are critical for maintaining balance and spatial orientation by detecting rotational movements.
Vestibular Sacs
Structures within the inner ear involved in the sense of balance, helping to detect changes in the position of the head.
Inner Ear
The innermost part of the ear, containing the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals, which is essential for hearing and balance.
Frequency Theory
A theory explaining the perception of pitch that asserts neurons fire at the same rate as the frequency of an auditory stimulus.
Q3: Two traveling waves, y<sub>1</sub> = A
Q7: A particle moves along the x axis.In
Q7: If = (2 m)− (3 m)and =
Q11: A solid wheel with mass M, radius
Q13: A 1-N pendulum bob is held
Q18: A 75-kg man is riding in a
Q22: A transverse traveling sinusoidal wave on a
Q36: A block of mass m is
Q49: The potential energy for the interaction between
Q50: Which of the curves on the