A radiometer has two square vanes (each measuring 1.0 cm by 1.0 cm) , attached to a light horizontal cross arm, and pivoted about a vertical axis through the center, as shown in the figure. The center of each vane is 6.0 cm from the axis. One vane is silvered and it reflects all radiant energy incident upon it. The other vane is blackened and it absorbs all incident radiant energy. An electromagnetic wave with an intensity of 0.30 kW/m2 is incident normally upon the vanes. What is the electromagnetic power absorbed by the blackened vane? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2) 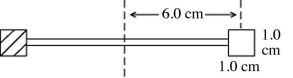
Definitions:
Hypothetical Syllogism (HS)
A logical argument formed by two conditional statements and a conclusion that follows from chaining the conditionals together.
Modus Ponens (MP)
A logical argument form that asserts if "P implies Q" and "P is true," then "Q must also be true."
Modus Tollens (MT)
A logical argument form where the denial of the consequent leads to the denial of the antecedent, often structured as "If P, then Q. Not Q, therefore not P."
Disjunctive Syllogism (DS)
A form of logical argument where, from two disjunct statements, the denial of one leads to the affirmation of the other.
Q3: For the circuit shown in the figure,
Q8: A 2.0 mm diameter wire of length
Q13: A refrigerator removes heat from the freezing
Q16: An object 1.25 cm tall is placed
Q18: As shown in the figure, a rectangular
Q22: A point charge Q = -500 nC
Q23: A ray of light consisting of blue
Q30: Consider the circuit shown in the figure.
Q30: If a nucleus decays by β<sup>- </sup>decay
Q35: An irregular conductor carries a surface charge