An uncharged 1.0-μF capacitor is connected in series with a 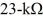 resistor, an ideal
resistor, an ideal  battery, and an open switch. What is the voltage across the capacitor
battery, and an open switch. What is the voltage across the capacitor 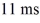 after closing the switch?
after closing the switch?
Definitions:
Marginal Cost Curve
A graphical representation showing how the cost to produce one additional unit changes as more units are produced.
Long-Run Supply
A period sufficient for all inputs to production, including capital, to be varied, allowing for adjustments to changes in demand or technology.
Average Total Cost
The total cost of production divided by the total quantity produced, representing the per-unit cost of production.
Long-Run Equilibrium
A state in which all factors of production and economic variables are in balance, with no external pressures forcing change.
Q3: The graph in the figure shows the
Q6: Two equal positive charges are held in
Q7: The figure shows two unequal point charges,
Q15: A container is filled with a mixture
Q16: As shown in the figure, two long
Q19: Consider a spherical Gaussian surface of radius
Q26: The long straight wire in the figure
Q26: What is the minimum magnitude of an
Q35: A 5.0-liter gas tank holds 1.4 moles
Q92: Two experimental runs are performed to determine