A charge q = 2.00 μC is placed at the origin in a region where there is already a uniform electric field 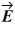 = (100 N/C)
= (100 N/C)  . Calculate the flux of the net electric field through a Gaussian sphere of radius
. Calculate the flux of the net electric field through a Gaussian sphere of radius 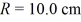 centered at the origin. (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
centered at the origin. (ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
Definitions:
Permeable
Capable of allowing fluids or gases to pass through it.
K+
Potassium ion, a key electrolyte in the body involved in nerve function, muscle contraction, and fluid balance.
Leak Ion Channels
Channels in cell membranes that allow ions to pass through without the need for stimulus, balancing cellular ion concentrations and membrane potentials.
Myofilament
Protein filaments, including actin and myosin, that are the fundamental components of muscle contraction.
Q1: An ice cube at 0°C is placed
Q3: You want to insert an aluminum rod,
Q3: A container is filled with a mixture
Q11: The mean free path of an oxygen
Q29: A charge of 1.0 × 10<sup>-6</sup> μC
Q30: An air-filled capacitor stores a potential energy
Q39: A 4.0-μF capacitor that is initially uncharged
Q43: The intensity of sunlight falling on the
Q45: A rod has a length 2.00000 m
Q96: The process shown in the pV diagram