The figure (not to scale) shows a pV diagram for 1.8 g of helium gas (He) that undergoes the process 1 → 2 → 3. Find the value of V3. The ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 J/mol ∙ K = 0.0821 L ∙ atm/mol ∙ K, and the atomic weight of helium is 4.0 g/mol. 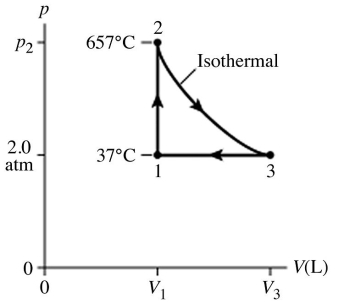
Definitions:
Absorption Costing
A costing method that includes all manufacturing costs—direct materials, direct labor, and both variable and fixed manufacturing overhead—in the cost of goods sold.
Variable Costing
An accounting method that includes only variable production costs (direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead) in product costs, excluding fixed overhead.
Units Manufactured
The total quantity of products completed and ready for sale or use at the end of an accounting period.
Variable Costing
A costing method where only variable production costs are assigned to inventory and fixed overhead expenses are treated as period costs.
Q4: The capacitive network shown in the figure
Q7: An ideal gas is kept in a
Q18: A 4.00-Ω resistor, an 8.00-Ω resistor, and
Q20: Fluid fills the container shown in the
Q25: A transverse wave traveling along a string
Q31: Two thin 80.0-cm rods are oriented at
Q39: An object of mass 8.0 kg is
Q40: An expansion process on an ideal diatomic
Q50: A board that is 20.0 cm wide,
Q89: If we use 67 W of power