A monatomic ideal gas undergoes an isothermal expansion at 300 K, as the volume increased from 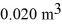 to
to 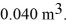 The final pressure is
The final pressure is 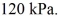 The ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 J/mol ∙ K. The heat transfer to the gas is closest to
The ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 J/mol ∙ K. The heat transfer to the gas is closest to
Definitions:
Anthocerophyta
Anthocerophyta is a phylum consisting of hornworts, a group of non-vascular plants that are characterized by their horn-like sporophytes and a simple, thalloid gametophyte.
Club Mosses
Ancient group of non-flowering plants with a vascular system, resembling mosses but genetically closer to ferns.
Lycopodiophyta
A division of vascular plants, also known as clubmosses, that are characterized by their leafy stems and cone-like structures.
Pteridophyta
Pteridophyta refers to a group of vascular plants that reproduce via spores and do not produce flowers or seeds, commonly known as ferns.
Q3: You want to insert an aluminum rod,
Q3: A 1.30-m long gas column that is
Q21: Which statements are true for an electron
Q23: Consider a very small hole in the
Q25: In the figure, a ring 0.71 m
Q31: Two thin 80.0-cm rods are oriented at
Q33: The cube of insulating material shown in
Q50: In an isochoric process, the internal (thermal)
Q63: The figure shows two long, parallel current-carrying
Q77: An 82.0 kg-diver stands at the edge