A fixed amount of ideal gas goes through a process abc. In state a, the temperature of the gas is 152°C, its pressure is 1.25 atm, and it occupies a volume of 0.250 m3. It then undergoes an isothermal expansion to state b that doubles its volume, followed by an isobaric compression back to its original volume at state c. (Hint: First show this process on a pV diagram.) The ideal gas constant is 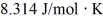 , and 1.00 atm = 1.01 × 105 Pa.
, and 1.00 atm = 1.01 × 105 Pa.
(a) How many moles does this gas contain?
(b) What is the change in the internal energy of the gas between states a and b?
(c) What is the net work done on (or by) this gas during the entire process?
(d) What is the temperature of the gas in state c?
Definitions:
Erosion Cost
Costs that occur when the introduction of a new project or product negatively impacts the sales and profits of existing products.
Upgrade
The process of replacing a product with a newer version or installing a newer version of software to improve functionality or performance.
Repair
The action of fixing or restoring something that is broken or damaged back to its original condition.
Equivalent Annual Cost
A financial analysis tool used to compare the cost effectiveness of two or more alternative investments, taking into account both the initial investment and the annual operating costs.
Q11: The figure shows the cross-section of a
Q15: A howler monkey is the loudest land
Q15: Three point charges are placed on the
Q22: A narrow copper wire of length L
Q24: A 905-g meteor impacts the earth at
Q25: You want to design an ideal Carnot
Q46: A 2.0-m string is fixed at both
Q47: In a certain region, the electric potential
Q48: In simple harmonic motion, the speed is
Q58: A uniform solid sphere is rolling without