A 1.86-kg block is held in place against the spring by a 81-N horizontal external force (see the figure) . The external force is removed, and the block is projected with a velocity v1 = 1.2 m/s upon separation from the spring. The block descends a ramp and has a velocity 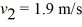 at the bottom. The track is frictionless between points A and B. The block enters a rough section at B, extending to E. The coefficient of kinetic friction over this section is 0.28. The velocity of the block is v3 = 1.4 m/s at C. The block moves on to D, where it stops. The height h of the ramp is closest to
at the bottom. The track is frictionless between points A and B. The block enters a rough section at B, extending to E. The coefficient of kinetic friction over this section is 0.28. The velocity of the block is v3 = 1.4 m/s at C. The block moves on to D, where it stops. The height h of the ramp is closest to 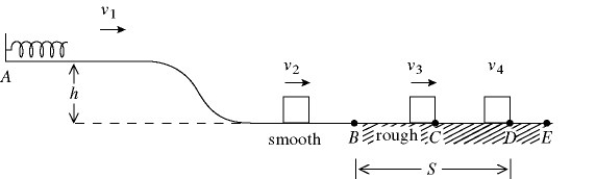
Definitions:
Ecological Approach
A perspective within psychology and other social sciences that emphasizes the importance of understanding individuals in the context of their physical and social environments.
Interdependence
A mutual reliance between two or more groups or people, where each is dependent on the others for certain needs or outcomes.
Mental Health
Narrowly, the absence of disorder. In a broader view, the presence of optimal social, emotional, and cognitive functioning—also known as wellness.
General Risk Factors
Conditions or variables associated with an increased likelihood of developing a disorder, illness, or other negative outcomes.
Q4: The current definition of the standard second
Q20: The figure shows the displacement y of
Q22: A system comprising blocks, a light frictionless
Q22: Two objects of the same mass move
Q27: Two boxes are connected by a weightless
Q30: Two identical ladders are 3.0 m long
Q32: If, in a parallel universe, π has
Q34: A sealed 89- <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7476/.jpg" alt="A sealed
Q44: The sound from a single source can
Q123: Which of the following would increase the