Figure 4-14 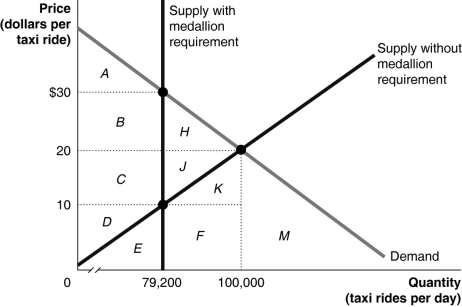 Figure 4-14 shows the market for taxi rides. The following question(s) are based on this figure.
Figure 4-14 shows the market for taxi rides. The following question(s) are based on this figure.
-Refer to Figure 4-14. To legally drive a taxicab in New York City, you must have a medallion issued by the city government. Assume that only 13,200 medallions have been issued. Let's also assume this puts an absolute limit on the number of taxi rides that can be supplied in New York City on any day, because no one breaks the law by driving a taxi without a medallion. Assume as well that each taxi provides 6 trips per day. In that case, the quantity of taxi rides supplied is 79,200 (or 6 rides per taxi × 13,200 taxis). This is shown in the diagram with a vertical line at this quantity. Assume that there are no government controls on the prices that drivers can charge for rides.
a. What would the equilibrium price and quantity be in this market if there was no medallion requirement?
b. If there was no medallion requirement, indicate the area that represents consumer surplus.
c. If there was no medallion requirement, indicate the area that represents producer surplus.
d. If there was no medallion requirement, indicate the area that represents economic surplus.
e. What are the price and quantity with the medallion requirement?
f. With a medallion requirement in place, what area represents consumer surplus?
g. With a medallion requirement in place, what area represents producer surplus?
h. With a medallion requirement in place, what area represents the deadweight loss?
i. Based on your answers to parts (c) and (g), are taxicab drivers better off with the medallion requirement for taxicabs than without?
j. Are consumers better off with or without the medallion requirement for taxicabs?
Definitions:
Pareto Optimal Allocation
A distribution of resources in which it is impossible to make any individual better off without making at least one individual worse off.
Endowed
Provided with a large amount of a resource or quality, often referring to financial grants given to institutions or individuals.
Units
The basic quantity or measurement, such as meter, kilogram, or liter, in terms of which something is considered or measured.
Quasilinear Utility Functions
Utility functions where consumers' utility is linear in one argument, typically representing money, allowing for easy analysis of changes in wealth.
Q21: Refer to Figure 4-3. What is the
Q31: Monique buys a new television for $795.
Q92: Use the following supply schedule for cherries
Q95: Which of the following is a result
Q189: If an increase in income leads to
Q212: Increases in the minimum wage are intended
Q229: The incidence of a tax depends on
Q267: Refer to Figure 3-4. If the price
Q315: Refer to Figure 3-7. Assume that the
Q461: If, in response to an increase in