The following is a system of simultaneous linear equations to allocate costs using the reciprocal method. Matrix algebra is not required.
The following costs were incurred in three operating departments and three service departments in Westmoreland Company.
Use of services by other departments is as follows.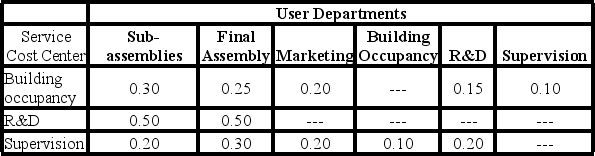
-
The equation for department S1 (building occupancy) is:
Definitions:
Income Statement
A financial statement that shows a company's revenues and expenses over a specific period, culminating in the net income or loss for that period.
Average Rates
A method for determining a consistent rate over a specified period, often used in calculations regarding finance or foreign exchange.
Foreign Subsidiary
An overseas entity controlled by a parent company, engaging in business operations distinct from those of the parent company in its home country.
Functional Currency
The main currency used by a business or economy, where the majority of its transactions are conducted.
Q26: The production budget allows management to plan
Q34: Which one of the following accounts is
Q68: Data Master is a computer software consulting
Q81: Last year, Jasmine Taylor opened a gift
Q96: It is possible to apply activity-based costing
Q96: Decentralization is lauded as important to good
Q110: <br>What are the equivalent units of production
Q115: The Country Garden Company's current net operating
Q122: Categorize each of the following quality activities
Q133: Nebraska Company uses the weighted-average method in