As shown in the figure, a 1.45-kg block is held in place against the spring by a 21-N horizontal external force. The external force is removed, and the block is projected with a velocity as it separates from the spring. The block descends a ramp and has a velocity at the bottom. The track is frictionless between points A and B. The block enters a rough section at B, extending to E. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the rough surface is 0.29. The velocity of the block is at C. The block moves on to D, where it stops. How much work is done by friction between points B and C? 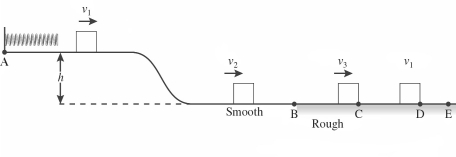
Definitions:
Formal Authority
The power granted to an individual or organization by virtue of position or role, allowing them to make decisions and enforce rules.
Coping With Uncertainty
The methods and strategies individuals or organizations employ to manage and adapt to situations where outcomes are unpredictable or unknown.
Prevention
Actions or measures taken to stop something undesirable from happening, such as illness, error, or conflict.
Substitution
The act of replacing one element or factor with another, often in economic, mathematical, or chemical contexts.
Q4: A torque of 12 N ?
Q15: Which of the following are SI units
Q16: Suppose NASA wants a satellite to revolve
Q39: Which one of the following is an
Q61: A 15-kg child is sitting on a
Q75: A satellite orbits the Earth once every
Q81: The process shown on the pV diagram
Q82: The rotating systems shown in the figure
Q88: A child does 350 J of
Q89: A solid sphere and a solid cylinder,