The figure shows two vectors and , along with their magnitudes and directions. The vector is given by = - . 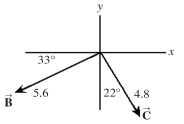 (a)What is the magnitude of vector ?
(a)What is the magnitude of vector ?
(b)What angle does vector make with the +x-axis?
Definitions:
Imperfect Competitor
An entity in a market that does not hold enough power to dictate the conditions of the market but can influence the price and output of its goods to some extent.
MRP
Marginal Revenue Product, the additional revenue generated from employing one more unit of a factor of production.
Unit of Input
The smallest measure of an input (like labour, materials) used in the production of goods or services.
Complementary Resources
Assets or inputs that are used together with another resource to produce a good or service, enhancing each other's value in the process.
Q7: A girl throws a rock horizontally with
Q15: Estimate the number of times an
Q25: Two boxes are connected to each other
Q26: Estimate the thickness, in meters, of an
Q64: You push downward on a trunk
Q74: The following conversion equivalents are given: 1.0
Q77: The mass of Pluto is 1.31 ×
Q82: The rotating systems shown in the figure
Q85: Vector <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\overrightarrow {
Q151: A 10-kg rock and a 20-kg rock