Use the following information to answer the question. Math self- efficacy can be defined as one's belief in his or her own ability to perform mathematical tasks. A college math professor wishes to find out if her students' math self- efficacy matches reality. To do this she gives a math quiz then asks her students to rate their level of confidence in how well they did on the quiz. She plans to test whether those who had little confidence that they did well on the quiz actually performed worse than those who had a high level of confidence that they did well on the quiz. Shown below is the approximate sampling distribution of the difference in mean quiz scores. The table below shows the summary statistics for the two groups. Assume that all conditions for a randomization test have been satisfied.
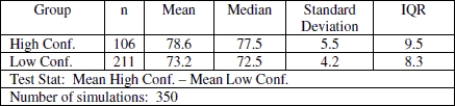
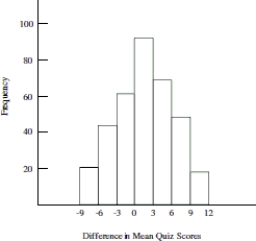
-Carry out the randomization test. What is the professor's conclusion? Are differences in mean quiz scores due to chance?
Definitions:
Milgram Experiment
A psychological experiment conducted by Stanley Milgram in the 1960s to study obedience to authority, where participants were instructed to administer electric shocks to another person.
Stanford University Prison Experiment
A psychological study conducted by Philip Zimbardo in 1971 at Stanford University, where students were assigned roles of prisoners and guards to explore the effects of perceived power.
Generalization
Drawing a conclusion about a certain characteristic of a population based on a sample from it.
Logical Support
The provision of reasons or evidence to justify a claim or argument.
Q7: A decrease in the cash rate<br>A)lowers the
Q11: Which of the following increases the quantity
Q16: A collection of twenty college students was
Q22: Test the hypothesis that the treatment is
Q24: Out of fifteen randomly selected people, how
Q40: Which of the following is true?<br>A)The demand
Q53: An ANOVA test was conducted to see
Q54: Compute the F- statistic. Round to the
Q73: Good A and good B are substitutes
Q101: If both the demand and supply increase,