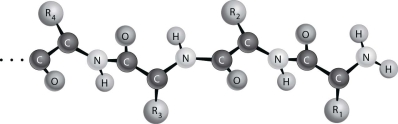
 Figure 2.2 depicts the (primary/secondary/tertiary) structure of a protein.
Figure 2.2 depicts the (primary/secondary/tertiary) structure of a protein.
Definitions:
Galactose
A simple sugar (monosaccharide) that, together with glucose, forms the disaccharide lactose; important in energy metabolism and found in dairy products.
Glucose
An elementary sugar critical for energy in living organisms and a key element of many carbohydrate compounds.
Principle Sugar
The primary type of sugar that is prevalent or most important within a particular context, such as glucose in human blood.
Nucleotides
Organic molecules that serve as the monomers, or building blocks, of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA, composed of a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and one or more phosphate groups.
Q5: Which property of antibodies is the basis
Q22: Among the areas of the female genital
Q34: The (constant/end/variable) regions from the light and
Q38: Hepatitis A does not cause chronic liver
Q47: Tuberculosis may be diagnosed using<br>A) immunoelectrophoresis.<br>B) a
Q49: A man has difficulty breathing, a cough,
Q52: Undiagnosed or untreated infections with Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Q56: What differentiates virulent strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae
Q65: Chronic inhalation of particular fungal allergens would
Q67: Parasitic diseases have been considered uncommon in