The following questions refer to the evolutionary tree in the figure below.
The horizontal axis of the cladogram depicted below is a timeline that extends from 100,000 years ago to the present; the vertical axis represents nothing in particular. The labeled branch points on the tree (V-Z) represent various common ancestors. Let's say that only since 50,000 years ago has there been enough variation between the lineages depicted here to separate them into distinct species, and only the tips of the lineages on this tree represent distinct species.
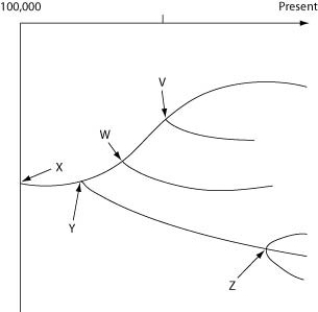
-Which of the five common ancestors, labeled V-Z, is the common ancestor of the greatest number of species, both living and extinct?
Definitions:
Preferred Activity
An activity that an individual chooses or prefers over other options, often used in reinforcement learning and behavior modification strategies.
Response Deprivation Theory
A theory suggesting that a behavior can become reinforcing when access to that behavior is restricted below its baseline level of occurrence.
Baseline Occurrence
The rate at which a behavior occurs before any intervention or conditioning is applied.
Probability-Differential Theory
The idea that an activity will have reinforcing properties when its probability of occurrence is greater than that of the reinforced activity.
Q1: Genomic imprinting is generally due to the
Q2: The Permian period ended and then rapid
Q9: If humans had been present to build
Q25: The following question is based on the
Q33: Use of synthetic fertilizers often leads to
Q33: Use the following description to answer the
Q35: In the form of gene therapy used
Q51: What essential information does the product of
Q66: If you were using cladistics to build
Q67: In the structural organization of many eukaryotic