Use the following figure and information to answer the question.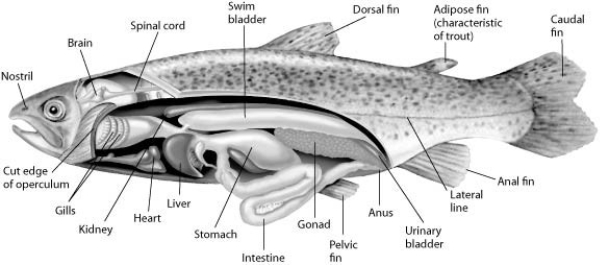
Fishes that have swim bladders can regulate their density and, thus, their buoyancy. There are two types of swim bladder: physostomous and physoclistous. The ancestral version is the physostomous version, in which the swim bladder is connected to the esophagus via a short tube (see the figure) . The fish fills this version by swimming to the surface, taking gulps of air, and directing them into the swim bladder. Air is removed from this version by "belching." The physoclistous version is more derived and has lost its connection to the esophagus. Instead, gas enters and leaves the swim bladder via special circulatory mechanisms within the wall of the swim bladder.
The presence of a swim bladder allows the typical ray-finned fish to stop swimming and still ________.
Definitions:
Sensory Neurons
Nerve cells responsible for converting external stimuli from the environment into internal electrical impulses for the brain to interpret.
Axons
Long, slender projections of nerve cells that transmit electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
Reflex Pathways
The neural circuits involved in involuntary responses to certain stimuli, enabling rapid reactions without conscious brain involvement.
Motor Neurons
Nerve cells forming part of the nervous system that transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to muscles or glands, causing them to act.
Q2: Shoot elongation in a growing bud is
Q19: Cottonwood, aspen, and willow trees have beige
Q21: Fossil fungi date back to the origin
Q42: Sperm cells are formed in plants by
Q51: Which of these events, based on plant
Q51: Including the membrane of the surrounding vesicle,
Q58: An individual mixotroph loses its plastids, yet
Q62: Heartwood and sapwood consist of _.<br>A) periderm<br>B)
Q65: Bulk flow is much faster than diffusion
Q71: Which of the following involves metabolic cooperation