Project 5.2 - Small Production Planning Project
(Fixed Charge Problem via Network Flow with Side Constraints)
Jack Small Enterprises runs two factories in Ohio, one in Toledo and one in Centerville. His factories produce a variety of products. Two of his product lines are polished wood clocks which he adorns with a regional theme. Naturally, clocks popular in the southwest are not as popular in the northeast, and vice versa. Each plant makes both of the clocks. These clocks are shipped to St Louis for distribution to the southeast and western states and to Pittsburg for distribution to the south and northeast.
Jack is considering streamlining his plants by removing certain production lines from certain plants. Among his options is potentially eliminating the clock production line at either the Toledo or the Centerville plant. Each plant carries a fixed operating cost for setting up the line and a unit production cost, both in terms of money and factory worker hours. This information is summarized in the table below.
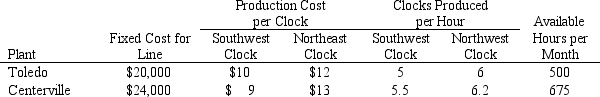 The Southwest clocks are sold for $23 each and the Northwest clocks are sold for $25 each. Demand rates used for production planning are 1875 Southwest clocks for sale out of the St Louis distribution center and 2000 Northeast clocks for sale out of the Pittsburg distribution center. Assume all these units are sold. The per clock transportation costs from plant to distribution center is given in the following table.
The Southwest clocks are sold for $23 each and the Northwest clocks are sold for $25 each. Demand rates used for production planning are 1875 Southwest clocks for sale out of the St Louis distribution center and 2000 Northeast clocks for sale out of the Pittsburg distribution center. Assume all these units are sold. The per clock transportation costs from plant to distribution center is given in the following table.
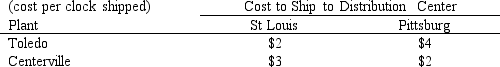 Develop a generalized network flow model for this problem and implement this model in solver. Use the model to answer the following questions.
Develop a generalized network flow model for this problem and implement this model in solver. Use the model to answer the following questions.
a.
Should any of the production lines be shut down?
b.
How should worker hours be allocated to produce the clocks to meet the demand forecasts? Are there any excess hours, and if so how many?
c.
What is the expected monthly profit?
d.
If a plant is closed, what are the estimated monthly savings?
Definitions:
Equilibrium Price
The trading value at which the supply of goods meets the consumers' demand for these goods.
Total Surplus
The sum of consumer and producer surplus, measuring the total net benefit to society from trading a good or service.
Supply
The total amount of a specific good or service that is available to consumers, typically influenced by the price level, production costs, and other factors.
Total Surplus
The sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus in a market, representing the total benefits to society from the production and consumption of goods and services.
Q6: Why do we create a scatter plot
Q7: Refer to Exhibit 11.1. What formula should
Q27: A network flow problem that allows gains
Q28: The following linear programming problem has
Q47: The MINIMAX objective<br>A) yields the smallest possible
Q48: The following network depicts an assignment/transportation problem
Q49: A manager engaged in the management function
Q56: The researcher would like to build a
Q107: Refer to Exhibit 11.20. What is the
Q122: At the death of her husband, Miriam