Project 9.1 - Test Stand Cost Analysis Estimation
Handel Manufacturing produces test stands for various maintenance functions ranging from automobile to jet airline testing stations. For years, their cost estimating function was based on a myriad of historical data fed into a cost analysis model that produced very accurate estimates of both development and support costs for various proposed test stands. James Mudd was a recent hire into the cost analysis shop. Unfortunately, during his first week on the job, James deleted the cost analysis database and failed to maintain a backup of the model. Fortunately, all is not lost. The computer support personnel can come in Monday and retrieve the model using their system backup tapes. Unfortunately, the cost proposals for three new test stand development and deployment projects are due first thing Monday morning. Since James recently left the company, you have been tasked to complete the cost estimate portion of the proposals.
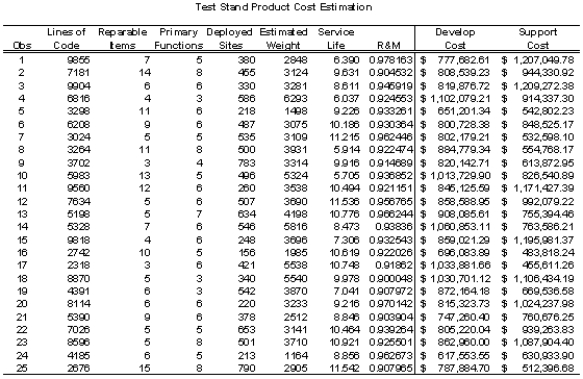
After much gnashing of your teeth, you settle down to make the best of what you initially believe is a losing situation. While studying James' files you find historical records on 25 recent test stand development and deployment projects. Rejuvenated, you realize you can succeed in this prematurely perceived doomed situation. All you need to do is analyze this historical data, develop some cost estimating functions using regression, and then use your regression models to develop estimates for the three projects due Monday. The historical data in the files is the following.
 The data estimates for the three cost proposal due Monday is the following:
The data estimates for the three cost proposal due Monday is the following:
One thing unclear from reading the files was on the form of the cost estimating relationships contained within the lost cost analysis model. You are somewhat sure the regression models were not polynomial in form, but you are not certain of this fact. You are not even sure which variables were included in the model for development cost and which variables were included in the model for support costs. However, you are undaunted because you know you can develop accurate models and produce good cost estimates for each of the proposed projects.
Develop appropriate models for development and for support costs. Use these models to develop cost estimates for each of the new lines of test stands. For each of these cost estimates provide 95% confidence intervals for the predicted values.
Definitions:
Operating Leverage
Refers to the extent to which fixed costs are used in a company's operations; high operating leverage means a larger proportion of fixed costs, leading to greater potential for profit variability with changes in sales volume.
Pretax Net Income
The amount of income that a company has earned before any taxes have been deducted.
CVP Analysis
Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis, a financial tool used to determine how changes in cost and volume affect a company's operating income and net income.
Pre-Tax Net Income
The income earned by a business before the deduction of tax expenses.
Q1: Project 14.1 <font face="symbol"></font> The Pre-Paid
Q4: The scores in a scoring model can
Q4: Refer to Exhibit 3.2. Which cells should
Q8: In generalized network flow problems<br>A) solutions may
Q19: The B & B algorithm solves ILP
Q19: Solve the following minimal spanning tree problem
Q26: A company wants to locate a
Q43: Refer to Exhibit 10.2. What is the
Q59: Which of the following is true regarding
Q90: Refer to Exhibit 14.9. What formula should