Project 12.1- Monte Carlo Integration
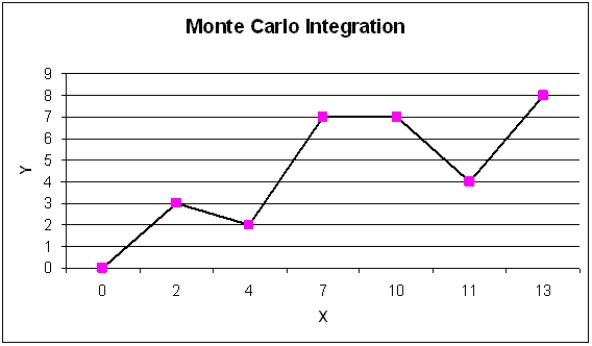
A common application of Monte Carlo simulation is to provide numerical approximations. One such application is to approximate the area under a curve, or Monte Carlo integration. The following figure represents such a curve, defined over the range of X = 0 to X = 13. Call the area under this curve A.
Monte Carlo integration begins by overlaying on the curve of interest a region (call this region, B) whose area is easy to calculate (i.e., a box). Monte Carlo integration then involves the random generation of points in B and a determination of the percentage of these points that fall in A (i.e., fall below the curve). This percentage represents that portion of the area of B that is the area of A.
Use Monte Carlo integration techniques to approximate the area under the curve. Use exact techniques to calculate the true area under the curve. How accurate is your approximation?
Definitions:
Solvency Risk
The risk that a company will not have enough funds to meet its long-term liabilities and financial commitments.
Long-term Asset Turnover Ratio
A financial metric that measures a company's efficiency in using its long-term assets to generate revenue.
Efficiency Gains
Improvement in the performance of a task, process, or system that leads to a reduction in resource usage, cost, or time required.
Z-score Model
The Z-score model is a financial model that predicts the probability of bankruptcy of a firm based on various balance sheet figures and market measures.
Q2: Subjective forecasting models are best characterized by:<br>A)
Q5: The term "time zero" identifies<br>A) the start
Q6: When yield management is implemented which one
Q22: Refer to Exhibit 10.7. Based on
Q34: Refer to Exhibit 10.4. Compute the discriminant
Q42: Refer to Exhibit 11.7. What are
Q51: Refer to Exhibit 10.1. What is the
Q55: Which of the following do not help
Q73: Refer to Exhibit 14.9. Assume the formula
Q85: Refer to Exhibit 14.9. What decision should