A post office requires different numbers of full-time employees on different days of the week. The number of full-time employees required each day is given in the table below. 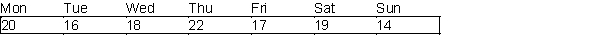 Union rules state that each full-time employee must work five consecutive days and then receive two days off. The post office wants to meet its daily requirements using only full-time employees. Its objective is to minimize the number of full-time employees that must be hired.
Union rules state that each full-time employee must work five consecutive days and then receive two days off. The post office wants to meet its daily requirements using only full-time employees. Its objective is to minimize the number of full-time employees that must be hired.
-(A) Use Solver to formulate and solve the post office's problem.
(B) Suppose the post office has 30 full-time employees and is not allowed to hire or fire any employees. Determine a schedule that maximizes the number of weekend days off received by the employees.
Definitions:
Monopolistically Competitive
A market structure where many companies sell products that are similar but not identical.
Monopolies
Market structures characterized by a single seller controlling a large portion of the market and the lack of viable competition.
Long-run Equilibrium
A state in which all factors of production and market forces are in balance, with no external pressures prompting change.
P = MR
An equality indicating that a firm's price (P) is equal to its marginal revenue (MR), often associated with perfect competition and profit maximization strategies.
Q11: Clustering is considered a supervised data mining
Q32: A global optimal solution is not necessarily
Q59: Uncertain timing and the events that follow
Q59: Which of the following statements is/are true
Q69: Which of the following statements are false
Q77: In a transshipment problem, shipments:<br>A) can occur
Q79: If the coefficient of correlation r =
Q81: Subjective probability is the probability that a
Q89: There are four quartiles that divide the
Q90: A statistician is currently trying to maximize