Suppose that simple exponential smoothing with 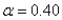 is used to forecast monthly wine sales at a liquor store. After April's demand is observed, the forecasted demand for May is 4500 bottles of wine.
is used to forecast monthly wine sales at a liquor store. After April's demand is observed, the forecasted demand for May is 4500 bottles of wine.
-(A) At the beginning of May, what is the forecast of July's wine sales?
(B) Suppose that actual demands during May and June are as follows: May, 5000 bottle of wine; June 4000 bottle of wine. After observing June's demand, what is the forecast for July's demand?
(C) Based on the data from (B), the demands during May and June average (5000+4000)/2 = 4500 bottle per month. This is the same as the forecast for monthly sales before we observed the May and June data. Yet after we observe the May and June demands for wine, our forecast for July demand has decreased from what it was at the end of April. Why?
Definitions:
Mind Wandering
A cognitive process where attention drifts away from a task towards unrelated thoughts or fantasies, often reflecting the brain's default mode of operation.
Subliminal Perception
Subliminal perception is the processing of information by sensory systems without conscious awareness, typically used to refer to stimuli below the threshold of sensation.
Stream of Consciousness
A literary technique or cognitive process where thoughts and feelings are presented in a continuous, uninterrupted flow.
Unconscious Processing
Mental processes not directly accessible to awareness or consciousness, influencing thoughts, feelings, and actions without our explicit awareness.
Q28: In time series data, errors are often
Q47: (A) Determine how to minimize the cost
Q48: When formatting your résumé, you should use
Q51: In a simple linear regression problem, suppose
Q56: The time series component that reflects a
Q61: Whenever possible, take advantage of the many
Q74: Which of the following does not represent
Q84: The set of all values of the
Q98: Customer loyalty models are an example of
Q101: Integer programming (IP) models are optimization models