Suppose that simple exponential smoothing with 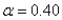 is used to forecast monthly wine sales at a liquor store. After April's demand is observed, the forecasted demand for May is 4500 bottles of wine.
is used to forecast monthly wine sales at a liquor store. After April's demand is observed, the forecasted demand for May is 4500 bottles of wine.
-(A) At the beginning of May, what is the forecast of July's wine sales?
(B) Suppose that actual demands during May and June are as follows: May, 5000 bottle of wine; June 4000 bottle of wine. After observing June's demand, what is the forecast for July's demand?
(C) Based on the data from (B), the demands during May and June average (5000+4000)/2 = 4500 bottle per month. This is the same as the forecast for monthly sales before we observed the May and June data. Yet after we observe the May and June demands for wine, our forecast for July demand has decreased from what it was at the end of April. Why?
Definitions:
Local Area Networks
A network of connected devices in a specific geographical location, such as a home or office, that share resources and data.
Intranet
A private network accessible only by an organization's staff, often used to share information, operational systems, or computing services within the organization.
Wireless Local Networks
A type of computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes to allow devices to connect to the internet or exchange data wirelessly over a short distance.
Hot Spots
Areas or places known for a high level of activity, interest, or risk, often used in the context of networking, tourism, or epidemiology.
Q10: (A) Determine how to minimize the total
Q14: Data analysis includes data description, data inference,
Q20: In transportation problem, shipping costs are often
Q20: It is wise to explore analysts' ratings
Q28: In time series data, errors are often
Q42: Forecasting software packages typically report several summary
Q57: Suppose a constraint has this equation: <img
Q63: In marketing models of customer loyalty, we
Q76: When attending a business-related conference, when is
Q133: Two advantages of printed handouts are that