Z is a standard normal random variable. Compute the following probabilities.
a.P(-1.33 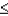 Z
Z 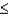 1.67)
1.67)
b.P(1.23 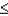 Z
Z 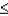 1.55)
1.55)
c.P(Z  2.32)
2.32)
d.P(Z  -2.08)
-2.08)
e.P(Z 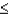 -1.08)
-1.08)
Definitions:
Quarterly Returns
The investment gains or losses experienced by an asset or portfolio over a three-month period.
Geometric Average Return
A method of calculating the average rate of return that accounts for the compounding of returns over time.
Quarterly Returns
The investment gains or losses recorded by a fund or portfolio over a three-month period.
Standard Deviation
A statistical measure of the dispersion or variability of a set of data points, often used in finance to quantify the risk associated with a specific investment.
Q5: Using an <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\alpha"><span
Q6: In a random sample of UTC students
Q15: Refer to Exhibit 8-2. If we
Q19: In interval estimation, the t distribution is
Q28: The milk prices (in quarts) from a
Q41: Random samples of size 525 are taken
Q85: Stratified random sampling is a method of
Q100: A random sample of 49 statistics examinations
Q105: The standard deviation of a sample was
Q151: In computing the mean of a