The combination of cold temperatures and wind speed determine what is called wind chill. The wind chill is a temperature that is the still-air equivalent of the combination of cold and wind. When the wind speed is 25 mph, the wind chill WC depends on the temperature t (in degrees Fahrenheit) according to 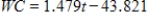 . For what temperatures does it feel at least 25°F colder than the air temperature? That is, find t such that
. For what temperatures does it feel at least 25°F colder than the air temperature? That is, find t such that 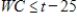 . Round your answer to two decimal places.
. Round your answer to two decimal places.
Definitions:
Null Hypothesis
A default statement that there is no effect or no difference, often used as a starting assumption in statistical hypothesis testing.
Type I Error
The error that occurs when the null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected, falsely indicating a significant effect.
Type II Error
Occurs when a false null hypothesis is not rejected, meaning an effect or difference is missed in the analysis.
Null Hypothesis
A default hypothesis that there is no significant difference or effect, used as the basis for statistical testing.
Q20: A polynomial is an expression of form
Q49: Find the exact real solutions to the
Q107: Use matrix F to find F<sup>2</sup>, if
Q108: If <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1243/.jpg" alt="If ,
Q188: If <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1243/.jpg" alt="If ,
Q189: Write the equation of the line passing
Q198: Use the matrices to find BA, if
Q238: Factor the expression completely. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1243/.jpg"
Q249: Rewrite the following so that only the
Q303: Simplify the complex fraction. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1243/.jpg"