If a test that has reliability r is lengthened by a factor 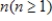 , the reliability R of the new test is given by
, the reliability R of the new test is given by 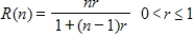
If the reliability is r = 0.6, the equation becomes 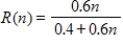 . When the test length is unchanged, the reliability r = R(1) = 0.6. If the length of the test is doubled, the reliability r = R(2) . What percent improvement is there in the reliability when the test length is doubled?
. When the test length is unchanged, the reliability r = R(1) = 0.6. If the length of the test is doubled, the reliability r = R(2) . What percent improvement is there in the reliability when the test length is doubled?
Definitions:
Avoidance Learning
is a process by which an individual learns a behavior or response to avoid a noxious or unpleasant situation or stimulus.
Aversive Event
An unpleasant or noxious stimulus that an organism seeks to avoid or escape, often used in aversive conditioning.
Matching Law
A principle stating that the proportion of responses on a particular schedule matches the proportion of reinforcements obtained on that schedule.
Maximizing Law
The principle that organisms will choose behaviors that maximize rewards and minimize penalties under conditions of uncertainty.
Q2: Your age group (1-9; 10-19; 20-29; 30-39;
Q64: In a pie chart, each slice is
Q65: Sketch the graph of the function <img
Q103: The given matrix is an augmented matrix
Q118: Each day, a young person should sleep
Q158: If <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1243/.jpg" alt="If ,
Q169: The percent of the U.S. population with
Q181: According to the U.S. Bureau of the
Q186: Perform the indicated operations and simplify.
Q216: Use a graphing utility with the standard