Suppose that the rate at which blood pressure decreases in the aorta of a normal adult after a heartbeat is 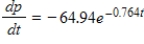 ,where t is the time in seconds. Use the function that describes the blood pressure in the aorta if
,where t is the time in seconds. Use the function that describes the blood pressure in the aorta if 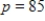 when
when 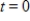 to find the blood pressure 0.9 second after a heartbeat. Round your answer to two decimal places.
to find the blood pressure 0.9 second after a heartbeat. Round your answer to two decimal places.
Definitions:
Payroll Tax Expense
The employer’s expense associated with the employment taxes (Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment taxes) on the wages paid to employees.
Federal Unemployment Taxes
Taxes paid by employers based on employee wages/salaries to fund unemployment compensation to workers who have lost their jobs.
Medical Insurance
Health care insurance for which premiums may be paid through a deduction from an employee’s paycheck.
State Income Tax
Taxes levied on income by individual states, varying widely in rate and structure from state to state.
Q6: In this problem, cost is in dollars
Q40: A chain of auto service stations has
Q48: If the supply function for x units
Q96: The graph of a company's total cost
Q115: At what y-value does the curve defined
Q118: Determine the most appropriate method or integral
Q119: Find any horizontal asymptotes for the given
Q128: Write the equation of the line tangent
Q153: Suppose that the weekly sales volume y
Q206: Find the indicated derivative and simplify.