The following income distribution data define points on Lorenz curves, where x represents the fraction of a certain country's population and L(x) the cumulative percent of income held by fraction x. Use this data and a numerical method to evaluate 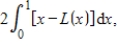 and hence to find the Gini coefficient of income for this country in 1995 and 2003. Round your answers to three decimal places.
and hence to find the Gini coefficient of income for this country in 1995 and 2003. Round your answers to three decimal places. 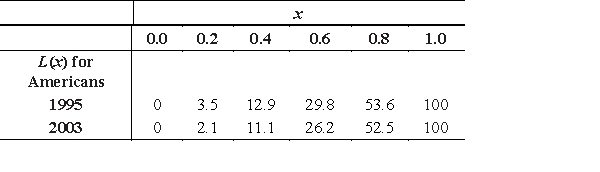
Definitions:
Personality Disorders
Types of mental disorders characterized by enduring maladaptive patterns of behavior, cognition, and inner experience.
Oedipal
Relating to the Oedipus complex, a concept in psychoanalytic theory referring to a child's unconscious sexual desire for the opposite-sex parent and jealousy toward the same-sex parent.
Electra Complex
The condition in which, according to Sigmund Freud, girls want to seduce their fathers to gain what they truly desire: a penis. By analogy to a character in several Greek tragedies.
Attachment Theory
A development of the psychoanalytic approach by John Bowlby. According to this view, children form attachments with their parents that become the child’s internalized model for all subsequent relationships. Difficulties in such attachments form the basis for later problems.
Q6: A rectangular box with a square base
Q11: The time series pattern that exists when
Q13: With nonprobabilistic sampling _.<br>A) it is possible
Q20: The rate of depreciation of a building
Q25: The probability of both sample information and
Q30: Consider the following data. <span
Q47: Find any vertical asymptotes for the given
Q58: SSE can never be _.<br>A) larger than
Q106: If $P is invested for n years
Q107: For a certain product, the total revenue